Key changes in ITR forms for AY 2017-18
Listen to this Article
Statistics laid out by the Finance Minister during Budget Speech 2017 regarding the number of tax payers in the country vis-a-vis quantum of expenditure incurred by individuals revealed a stark distinction between disclosure of income and expenditure. In order to the change the current scenario and bring about ease in disclosing income and filing of returns the government has taken a careful and mindful step in rolling out new ITR forms.
The single largest change in the new return forms notified is a simplified one pager form (ie ITR 1) for Individuals having income from salary, pension, one house property and income from other sources (ie, interest, etc). This will cover more than 90 percent of the taxpayers in the individual category like salaried class, housewifes, pensioners, etc. The form is shorter, less complicated and can be easily understood and filed by a common man without necessarily the assistance of a professional.
The return forms notified for FY 2017-18, their applicability and key changes are tabulated below:
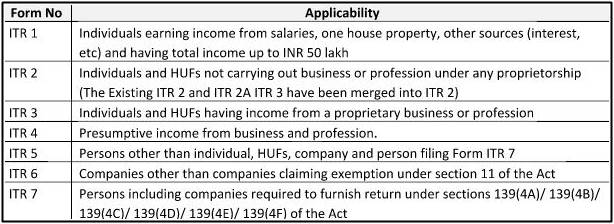
Key changes in the ITR Forms:
|
ITR Form No |
Key change |
Details |
| ITR 1, 2, 3 and 4 | Disclosure of Aadhaar number | Mentioning of Aadhaar number or the Aadhaar enrolment number (in case applied for) in the return form is compulsory |
| ITR 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7 | Disclosure of cash deposited between November 9, 2016 and December 30, 2016 | A new column has been inserted in all ITR forms to report cash deposited by taxpayers in their bank accounts during the demonetisation period (ie, from November 9, 2016 to December 30, 2016). However, taxpayers are required to fillup this column only if they have deposited cash in excess of INR 2 lakh during the demonetisation period |
| ITR 2, 3, 5, 6 and 7 | Unexplained income chargeable at special rates | New columns have been inserted under “Schedule OS” to report unexplained income which will be taxed at the rate of 60 percent |
| ITR 2, 3 and 4 | Deduction under section 80EE of the Act | Section 80EE allows deduction on home loan interest for first time home buyers to the extent of Rs 50,000. This deduction is over and above the Rs 200,000 limit currently permitted for house property covered under section 24(b) (ie, house property). A new field has been provided in the new ITR forms under Schedule VI-A deduction to claim home loan interest under Section 80EE of the Act |
| ITR 2, 3 and 4 | Additional details pertaining to assets and liabilities by Individuals/ HUFs earning above INR 50 lakh |
Last year the Government had introduced a new schedule requiring individuals/ HUFs to declare the value of assets and liabilities if their total income exceeds INR 50 lakh. Taxpayers were required to mention the cost of immovable property, jewelry, bullion, vehicles, shares, bank and cash balance, etc.
Taxpayers are now required to disclose description and address of the immovable property and movable assets in new ITR forms. Further, new fields have been introduced in ITR forms for disclosure of ‘Interest held in the assets of a firm or Association of Person (“AOP”) as a partner or member’. Such members/ partners are also required to disclose the name, address, PAN of the firm or AOP |
| ITR 3 and 5 | Details of Chartered Accountant (“CA”) firm conducting audit | Taxpayers are now required to disclose name and membership number of CA signing audit report along with name, registration number and PAN of audit firm in the new ITR forms |
| ITR 4 | Segregation of digital receipts and other receipts under presumptive taxation scheme | As per the presumptive taxation scheme provided under section 44AD of the Act, 8 percent of gross receipts or turnover is to be deemed as income of the taxpayer. However, Finance Act 2017 reduced this to 6 percent for digital receipts of the taxpayer. New columns have been inserted in ITR 4 to disclose turnover received through digital mode. Consequently, columns have been inserted to disclose presumptive income at 6 percent and 8 percent. |
The theme of the changes to the ITR forms seems to be “simplification” and changes such as removal of sections not regularly used by Individuals/ HUFs, reflection of digital and non-digital receipts in the presumptive income cases, reflection of with deduction under section 80EE are welcome moves.
While, however some changes such as further details in respect of assets (immovable property, jewelry, bullion, vehicles, shares, bank and cash balance, etc), interest in firms and AOPs, details of Chartered Accountants would increase the burden on taxpayers.
Disclosure of the deposits during demonization in the ITR has been made to ease identification of undisclosed incomes and substantial portion of the revenue’s audit efforts on the FY 2016-17 returns are likely to be focused on this part of the return. The linking of Aadhaar with PAN and invalidation of PAN where such linking is not done should result in a cleaning up of the multiple PAN per individual that has been said to be a significant road block in examining the demonization deposits.
Overall, the changes to the ITR forms are a welcome move and should result in a higher compliance ratio from taxpayers. #casansaar (Manoj N Kumar - Indian Express)
Category : ITR | Comments : 0 | Hits : 1858







Comments